Q.(1)- Current carrying solenoid is used as a bar-magnet. Describe it.
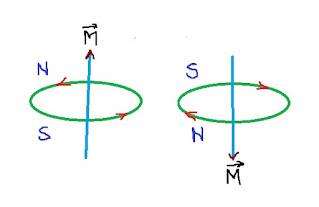
A current carrying solenoid produces magnetic field resemble to magnetic field of a bar magnet. The end of the current carrying solenoid where direction of current is clockwise acts as a south pole and the end of the current carrying solenoid where direction of current is anticlockwise acts as a north pole. So current carrying solenoid is used as a bar magnet.
Q.(2)- What is Lorentz force?
Bihar Board -2019 ,2022
Answer- Force on a charged particle placed in an electric and a magnetic field simultaneously is called Lorentz force.
also read- 12th Physics Short Question-Answer
If q charge is placed in electric
field $\vec{E}$
then electric
force on the charged particle
\[{{F}_{e}}=qE\]
\[{{\vec{F}}_{e}}=q\vec{E}\]
If q charge is placed in magnetic
field $\vec{B}$
then magnetic force on the charged particle
${{F}_{m}}=qVB\sin
\theta $
${{\vec{F}}_{m}}=q(\vec{V}\times \vec{B})$
Where v = velocity of the charged particle
\[\theta \]= angle between velocity of the charged particle and magnetic field
If q charge is placed in an electric and a magnetic both fields simultaneously then net force on the charged particle
$\vec{F}={{\vec{F}}_{e}}+{{\vec{F}}_{m}}$
$\vec{F}=q\left[
\vec{E}+\left( \vec{V}\times \vec{B} \right) \right]$
This is Lorentz Force.
Q.(3)- Write Fleming’s left hand rule.
Bihar Board -2020,2023
Answer- Three fingers of left hand thumb ,index finger and middle fingers are stretched mutually perpendicular . If index finger represents the direction of magnetic field, middle finger represents the direction of current then thumb will represent the direction force on(or motion of) the conductor.
OR
Magnetic poles of a galvanometer are cylindrical (concave) why?
Answer- Cylindrical magnetic poles are used in a galvanometer to keep its coil always in radial position. Due to which torque on the coil is
maximum, which is equal to nIAB .
Q.(5)- What is shunt ?
Bihar Board -2019
Write two uses of shunt.
Bihar Board -2015, 2019
Answer- Shunt is a low resistance conductor ,which is connected parallel to a
galvanometer or an ammeter to protect it from excess of current
Uses of shunt-
(i) Shunt is used to protect a galvanometer or an ammeter from excess of
current.
(ii) Shunt is used to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter .
(iii) Shunt is used to increase the range of an ammeter.
Q.(6)- What is difference between an ammeter and a voltmeter?
Answer- Ammeter
(i) Current is measured by ammeter.
(ii) Ammeter is connected in series
(iii) Its resistance is low.
Q.(7)- What type of force acts between two mobile charges?
Answer- If two charges are stationary then electric force acts between them.
But, if two charges are mobile then electric and magnetic both forces act between them.
Q.(8)- Write the force between two parallel currents.
Answer- $F=\frac{{{\mu }_{o}}}{2\pi }\frac{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{_{2}}}}{r}l$
Q.(9)- Why ammeter is connected in series, while voltmeter in parallel with main supply?
Answer- Ammeter is used to measure current. So it is connected in series so that whole current flows through it.
also read- NEET Numericals
Voltmeter is used to measure potential difference between two points (of the circuit) therefore it is connected in parallel to those two points.
Q.(10)- How will you change an ammeter into voltmeter?
Answer- At first we will remove shunt from it then connect a high resistance in series with it to change it into a voltmeter. Q.(11)- What is Bohr magneton ?
Answer- Bohr magneton is a small unit of magnetic dipole moment.
\[{{m}_{B}}=\frac{eh}{4\pi
m}=9.27\times {{10}^{-24}}J/T\]
Q.(12)- Applying Biot-savart’s law deduce the expression the for the magnetic
field at center of a semicircular loop of radius R carrying current I .
Bihar Board -2009
Let, there is a semicircular current carrying coil
of radius R carrying current I.
dl is an small element of the circular coil.
The magnetic
field at the center O of the coil due to the small element dl is dB.
A/C to Biot-Savart law
$dB=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}}{4\pi }\times \frac{Idl\sin {{90}^{\circ }}}{{{R}^{2}}}$
$dB=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}}{4\pi }\times \frac{Idl}{{{R}^{2}}}....\left( i \right)$
Now , magnetic field due to the whole
semiconductor coil .
$B=\int{dB=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi
R}{\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi }}}\times \frac{Idl}{{{R}^{2}}}$
\[B=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}}{4\pi }\times \frac{I}{{{R}^{2}}}\int\limits_{0}^{\pi R}{dl}\]
\[B=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}}{4\pi }\times \frac{I}{{{R}^{2}}}\left[ l \right]_{0}^{\pi R}\]
\[B=\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{4\pi
}\times \frac{I}{{{R}^{2}}}\left[ \pi R-0 \right]\]
\[B=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}}{4\pi }\times \frac{I}{{{R}^{2}}}\times \pi R\]
\[B=\frac{{{\mu
}_{0}}I}{4R}\]
This is magnetic field at the center of the given semi circular coil .















THIK H
ReplyDelete